
Neither does work in an anonymous digital environment, especially the verification is a challenge. Debit and Credit cards use PIN codes for verification but that requires a middle-man with terminals. Typically banks or notaries have signature-cards to prove that it is indeed you and not someone else. Hand-written signatures have been and still are a unique prove that you, and only you, signed a document or transaction. For now, remember that you always need a seed text to generate a hash. (FYI: Hash functions are designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and made available under a royalty-free license.) This process is irreversible, every key produced is unique and even the slightest change in the input generates a completely different key. (Observe the W and w difference). This key, also called the HASH, can be seen as the unique signature or fingerprint of that piece of text or information, but is also very usable to act as a unique transaction address/identifier in a blockchain. Hashing is a mathematical function (software coded) that converts an arbitrary text into a fixed length digital key. Let me start with explain hashing, a key-element in blockchain. Blockchain addresses and the control thereof is based on two key cryptographic elements: hashing and asymmetric digital signatures. He or she that can prove that an address/identifier is his or her’s has ownership of the transaction and its content or value. Transactions in a Blockchain are referenced by an address comparable with an identity or identifier. Bitcoin and Ethereum) that can be used by anyone in an anonymous way.
Leaves us with the permission-less or public versions (e.g. Private versions are typically for internal use within a company and not accessible from outside. For the use of a permissioned type you need to get admission from the organization that has built or maintains this Blockchain and normally they issue some kind of identity.
#Blockchain transaction verification pdf
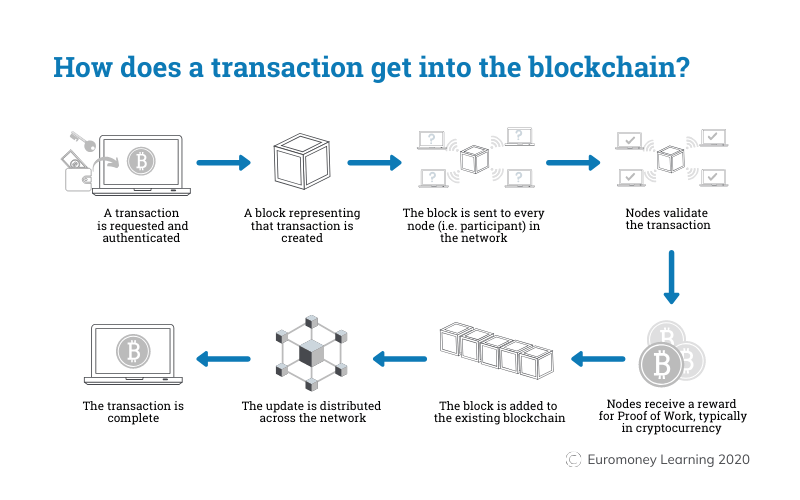
Also for this article, re-use is granted, keeping it “as is” and respecting the copyrights. (See below for downloads in OpenOffice and PDF format)īlockchains can be classified into three types Permission-less, Permissioned and Private. Be aware, cryptography is key in Blockchain and sometimes pretty hairy to follow, but with some simplification also very understandable for those who do not relate so much with mathematical functions. But what do you need to do to prove these transactions are yours without revealing your identity?Ī very relevant question as the technology for this in a typical blockchain is quite different from what most of us know as “user-id/password”.Ī picture is worth a thousand words, and for me the way to explain how this works in my favourite 3 step approach. These blocks contain many transactions which are supposed to be anonymous. In my previous article, I explained the mechanics of the Blockchain and how blocks are linked into an immutable chain with clever crypto functions. Ready to learn Blockchain? Browse courses like Blockchain for Finance Professionals developed by industry thought leaders and Experfy in Harvard Innovation Lab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
